Navigation auf uzh.ch
Navigation auf uzh.ch

Media companies are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) to produce news content. The launch of generative AI programs such as ChatGPT has further fueled this trend. Now for the first time, the fög has conducted a representative survey to investigate how the Swiss public feels about AI-produced media coverage.
Just under a third (29%) of respondents say they would read news items written entirely by AI. In comparison, 84% would read texts written by journalists without the use of AI. Acceptance varies by topic: for weather, sports news, stock-market prices or celebrity gossip, respondents would be more likely to consider reading AI-generated news, while for news about politics, the economy, science or culture, acceptance of AI is significantly lower.
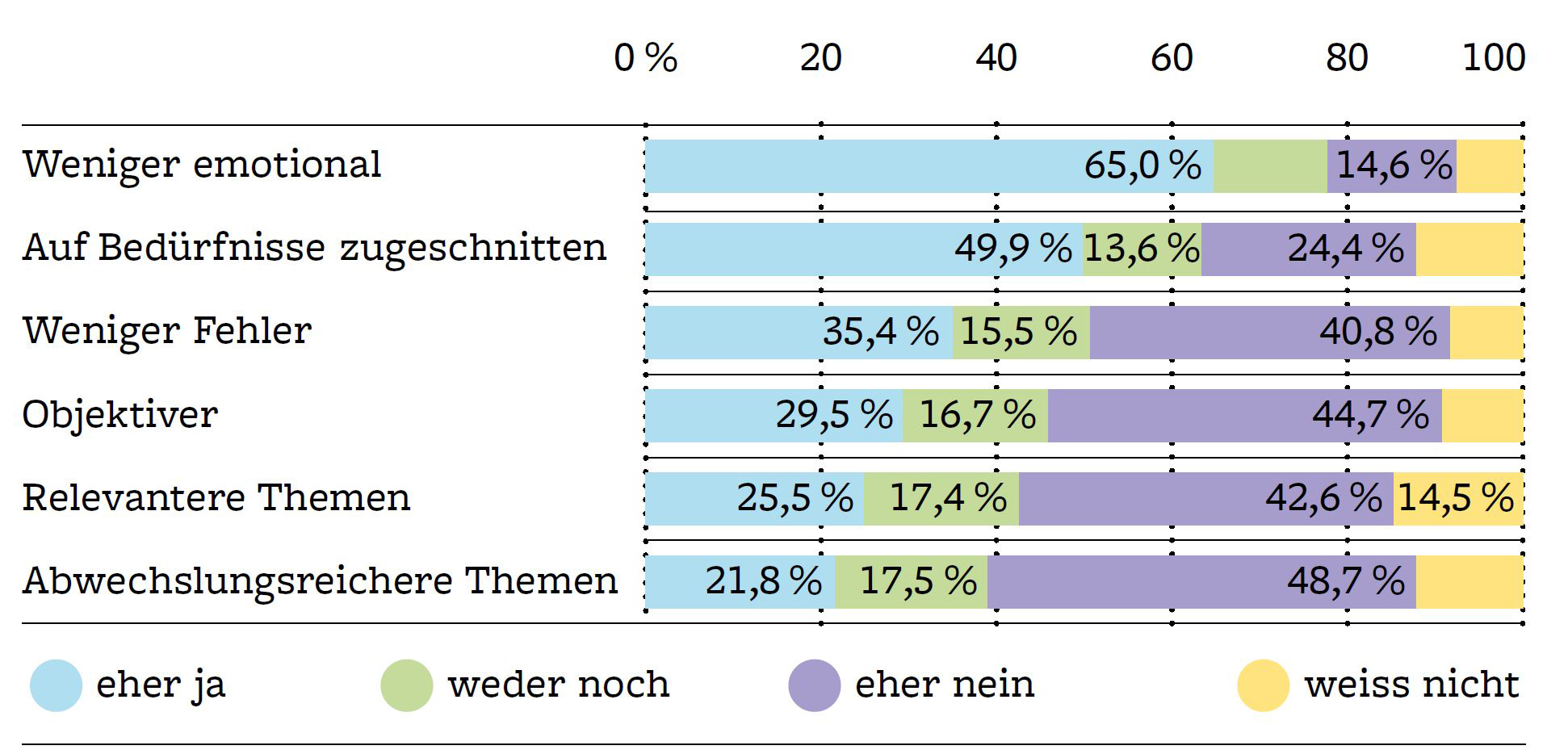
Well over half the Swiss population (61%) believes the overall quality of reporting will deteriorate if the use of AI to write articles increases. A clear majority fears it will lead to less diversity of opinion and more false information. Over 80% of respondents therefore also think content created in whole or in part by AI should be labeled accordingly. Until now, Swiss media companies have been reticent in this regard, and there are no industry-wide standards. “Swiss media companies should place a higher priority on declaring AI use,” says media expert and fög director Mark Eisenegger. “This is the only way serious journalism can differentiate itself from the growing number of dubious offerings that rely solely on generative AI.”
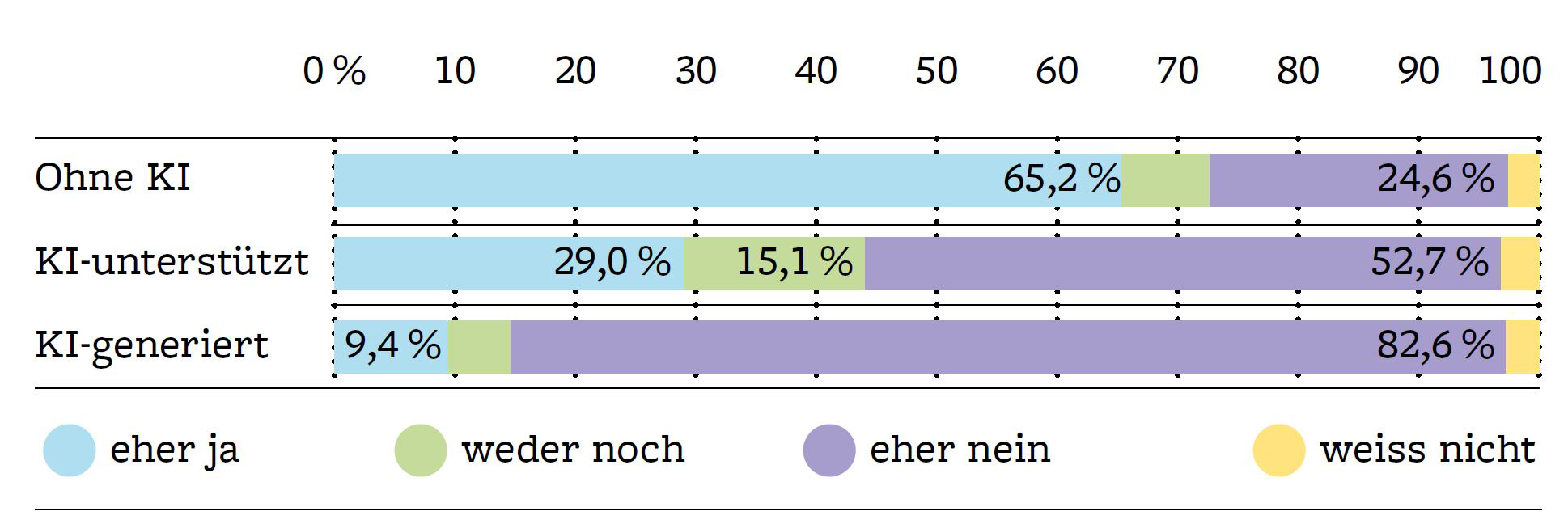
Only around 10% of respondents said they would be willing to pay for news articles written entirely by AI. In contrast, more than two thirds would pay for content written by journalists without the use of AI. One reason for the lack of willingness to pay for AI-produced content, alongside the presumed quality deficits, could be that most people associate the use of AI with lower costs and time savings for media companies. Still, a clear majority of those surveyed believe that media companies are entitled to compensation from AI providers if content written by their (human) journalists is used to train the automated systems. “This is an important finding, especially with regard to the current political debate on copyright laws,” says Mark Eisenegger.
Journalism in Switzerland faces other challenges, too: the number of people who hardly consume any news at all, known as the “news deprived”, continues to grow and now comprises 43% of the Swiss population. When asked about the type of news that they are interested in, many Swiss people mention “positive” or “constructive” journalism, i.e. good news stories or articles that discuss possible solutions alongside problems. An expansion of constructive journalism could therefore counteract the increase in news deprivation.
Despite the structural difficulties in journalism, there are also positive findings. The Yearbook’s long-term measurement of media quality found that it this year reached its highest level since 2015. Contributing factors were the coronavirus pandemic and the war in Ukraine. Due to these events, the relevance of media coverage increased – also in previous years – as the media focused more on politics. The Swiss media presence on TikTok and Instagram is also of relatively high quality. Although on both platforms soft news is prioritized and the tone is more emotional, the presentation of Swiss media posts on Instagram and TikTok provides more contextualization than content on websites offering a full news service, as a limited number of posts are produced specifically for the social media platforms.
The 2023 Yearbook Quality of the Media and accompanying in-depth studies are available at www.foeg.uzh.ch